1. Rectification: Rectifier diodes are mainly used in rectification circuits to convert alternating current into pulsating direct current. Common rectifier diodes are 1N4007, 1N5399 and 1N5408.

Two: voltage stabilization: this kind of tube is made by using the reverse breakdown characteristics of the diode, and it is connected in the circuit to keep the voltage at both ends of it basically unchanged, playing the role of stabilization. Common Zener diodes are 2CW55 and 2CW56.
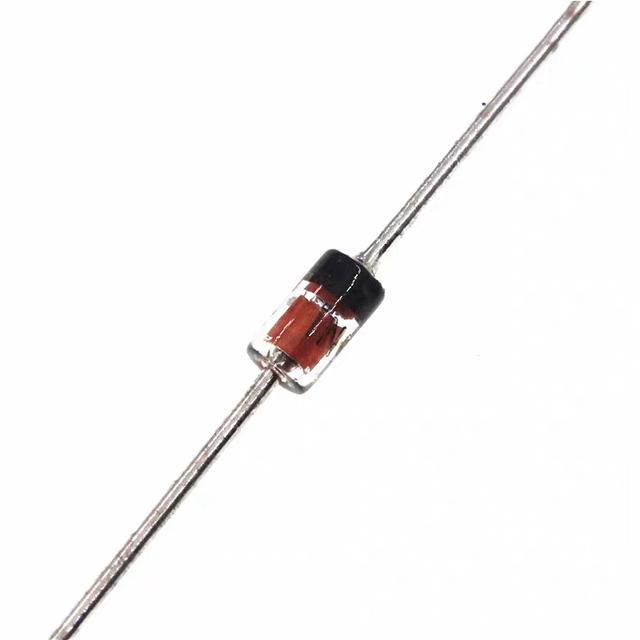

Three-switch diode: the diode has a small resistance under the forward action and is in the on state, which is equivalent to an on switch; under the reverse voltage, the resistance is very large and is in the off state, just like an off switch. The characteristics of diodes can form various logic circuits.
Four: Limiting. After the diode is turned on, its forward direction remains basically unchanged (silicon tube 0.7V germanium tube). Using this feature as a limiting element in the circuit, the signal amplitude can be limited within a certain range. Five: Freewheeling It plays a role of freewheeling in inductive loads such as the inductance and relay of the switching power supply.
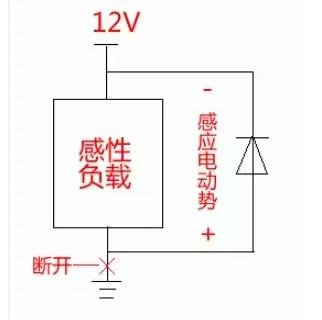
Six: Trigger Trigger diode, also known as bidirectional trigger diode, is a two-terminal semiconductor with a three-layer structure and symmetrical property. It is often used to trigger bidirectional thyristors for overvoltage protection in circuits.