Zener diode is a diode used to stabilize voltage and work in reverse breakdown state;
Zener diodes are mainly used in constant voltage sources, auxiliary power supplies and reference power circuits; in digital circuits, they are often used for level shifting; in overvoltage circuits, they are used for protection.
Zener diode (also known as Zener diode or reverse breakdown diode) is a surface contact type crystal diode made of silicon material. Its symbol is different from ordinary diodes, as shown in the figure below.
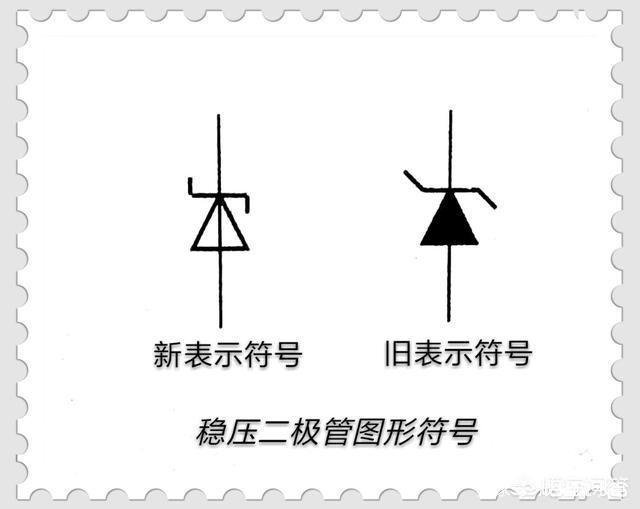
The silicon voltage regulator tube is different from ordinary diodes, and its working range is just taken in the breakdown area. The regulator tube can do this because it has the following two characteristics:
(1) It is allowed to work in the breakdown zone that does not exceed the maximum power dissipation
When working in the breakdown zone, as long as the reverse current through this tube is less than the maximum allowable current of this tube, or the power dissipated on this tube does not exceed the maximum power dissipation, the Zener tube will not burn out , It works normally.
(2) Zener tube has the characteristic of rapid breakdown under a certain voltage, as shown in the figure below.
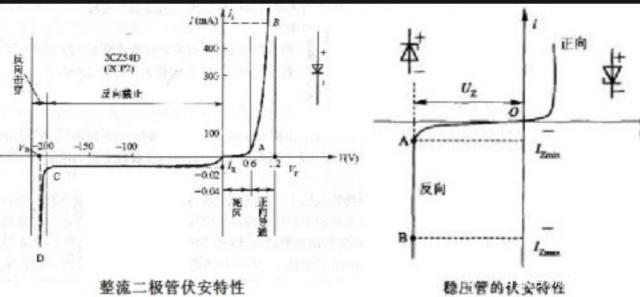
In general, a Zener tube is a semiconductor element with a high resistance until the critical reverse breakdown voltage. The voltage regulator tube has been working in the reverse breakdown zone in the electronic circuit, so its connection mode is just the opposite of that of the ordinary diode.
It can be seen from the above figure that the voltage regulator tube is almost constant within a certain current range, showing a very good voltage stabilization characteristics, so it is widely used in electronic circuits.
① Stable voltage Uz……In the stable range, the voltage on the regulator tube;
② Stable current Iz……refers to the current value with the best voltage regulation characteristics;
③Maximum stable current Izm……refers to the maximum current that the Zener diode is allowed to pass through;
④Maximum power dissipation Pzm...... Under the regulated voltage, when the current increases to a certain value Izm, the heat emitted in the tube will damage the tube;
⑤Dynamic resistance Rz……In the working area, the ratio of the voltage change at the two ends of the regulator tube to the current change, it changes with the operating point, and the smaller the value, the better.
The commonly used parameters of ordinary diodes are:
①The maximum rectified current Im, which refers to the maximum forward current value that the diode can pass through under normal conditions for a long time;
②Reverse current Ico, which refers to the direct current flowing through the diode when the diode is applied with a reverse voltage. In the ideal state, the diode has no reverse current due to its single-phase conductivity, but in actual work, it will have a small current flowing; the size of Ico reflects the quality of the single-phase conductivity of the diode, that is, the smaller the value of Ico, the The single-phase conductivity is better.
③Maximum reverse working voltage Urm, which refers to the maximum reverse voltage that the diode can withstand during normal operation. When the diode is reversely connected, when the reverse voltage reaches a certain fixed value, the reverse current in the diode will increase drastically, making the diode present a breakdown state. The voltage at this time is called the reverse breakdown voltage.
Zener diode in kind
④ The highest operating frequency Fm refers to the frequency at which the diode works in the circuit. Due to the different manufacturing process, materials and structure of the diode, the operating frequency of the diode is also different. In the high-frequency rectifier circuit, if this characteristic of the diode cannot meet the conditions , The diode will heat up severely and lose its single-phase conductivity.